

In this article we introduce what Business Process Management (BPM) is and why it is important. BPM refers to the specific framework required to control and ensure strategic development of the company’s processes. The framework was developed by Michael Hammer, professor at MIT.
First, let’s look at why BPM is important – that is, the motivation to start on the path to excellent management of business processes.
Businesses create value for their customers and their owners through their processes. It is in the processes that the potential for improvement and development exists. It is also in the processes that you find important risk factors for not reaching strategic goals.
This is also described in our free guideline How to Introduce a Business Improvement System for Download.
BPM as we have defined it above is thus about having control over value creation and further developing it. This overall perspective on BPM should alone be sufficient to create a curiosity about what it is and how to go about developing existing process management practices. If we go a little deeper into the matter, we will be able to identify even more benefits.
In a situation with outstanding process management practices, the company has a visual image of the processes and their relationships. This visualization is called a process model. The business will also have a visual, understood and realistic picture of planned future state (state process) for the process model. The company also regularly manages the desired long-term version of the process model (super future state). Future state and super future state versions of the process model are consequences of strategic assessments (conclusions in the strategy process). For example, strategic assessments may lead the company to realize that one must significantly reduce time-to-market and the cost of products and services.
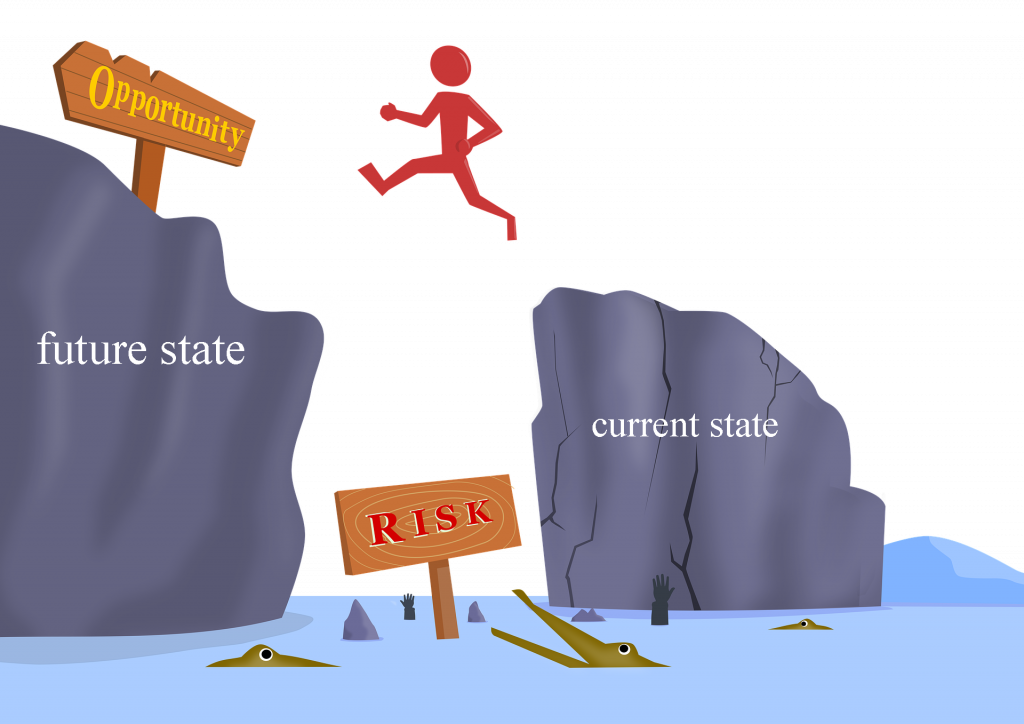
The “strategic” gap between the current situation and the future situation for the process model defines the business needs and thus the future state for organizational development. It is this business need that should form the basis for investment in human and structural capital. In such an approach, the IT strategy will be based on the business process needs, short term and long term.
The HR strategy for employee and managerial development can be based on the same business need. Competence development will thus appear more as an investment in future competitiveness than a cost.
There are several important reasons why the business should have a plan to reach an excellent level of process management. We are pleased to mention another important advantage.
Effective process management means that you have fact-based control of the processes. This not only enables fact-based improvement work on individual processes, but also fact-based end-to-end improvement for the company’s products and services. Fact-based insight makes it possible to specify the ambition of business case-driven identification of improvement needs.
Based on the arguments above, it is obvious that companies with ambitions for outstanding results should have BPM high on the management’s agenda.
Finally, let’s take a closer look at the content of BPM.
BPM includes specific proposals for structures to control and improve the processes. Important content is:
The BPM theories were originally described by Ph.D Michael Hammer at MIT. He also described the theories of Business Process Reengineering (BPR).
A visual process model identifies all the business processes needed to create value for its customers and owners. The model also describes the most important relationships:
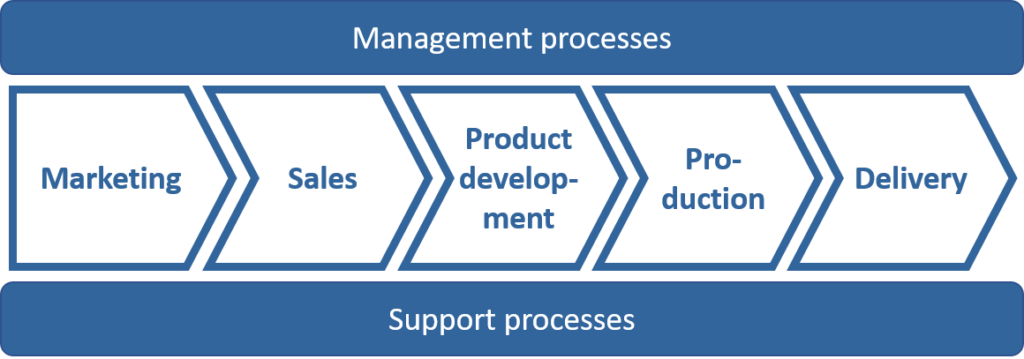
In quality systems, the business processes are often grouped into the main processes (arrows in the middle), management and support processes. The figure illustrates this. Such visualizations are common, but do not meet the requirements of a process model that should include the relationships specified above.
An important responsibility that the process owner has is to establish improvement structures that meet both the ongoing operational needs, and also the strategic needs. For the main processes and important other processes, the development of the future state should include Michael Hammer’s BPR approach. This approach has proven to be able to identify opportunities that require further development of the company’s business model(s).
The company’s Business Improvement System (BIS) is a specification of how to work with internal business development. BIS provides answers to how one develops/improves the business processes and products/services. If you have not already read about BIS, you can check out our post “Aksena’s Proposal for Business Improvement System” or download our free guide on how to implement a BIS in you company:


